| Molbank 2004, M381 |
Petra P¨¢d¨¢r, Györgyi Kov¨¢cs and Lajos Kov¨¢cs*
Department of Medicinal Chemistry, University of Szeged, D¨®m t¨¦r 8, H-6720 Szeged, Hungary.
Fax: +36-62-54 59 71
*E-mail: [email protected]
Received: 16 October 2003 / Accepted: 17 March 2004 / Published: 29 March 2004

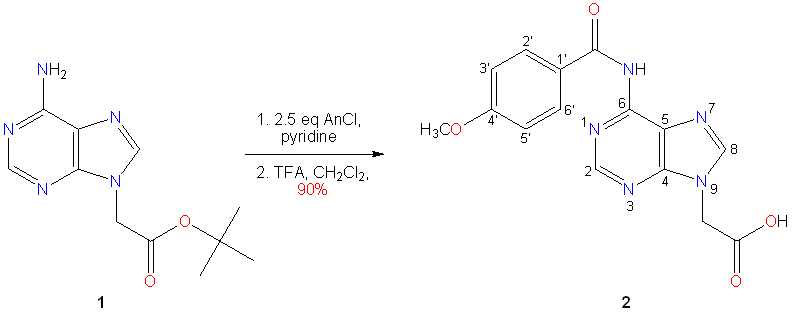
{6-[(4-Methoxybenzoyl)amino]-9H-purin-9-yl}acetic acid 2 is one of the substances used in the synthesis of peptide nucleic acid (PNA) adenine monomer and oligomers as well. In our previous work [1] the title acid 2 was prepared by controlled basic hydrolysis of the corresponding N6,N6-dianisoylated ethyl ester derivative. The pH of this reaction solution was carefully maintained to prevent undesired hydrolysis of the N6-(4-methoxybenzoyl) (anisoyl) protecting group which reduced the yield. In our present approach we have chosen the tert-butyl ester 1 as starting material [2] for anisoylation and the resulting N6,N6-dianisoylated substance was subjected to acidic hydrolysis to afford compound 2 in an excellent overall yield. In this latter step the simultaneous removal of one anisoyl and tert-butyl groups happened.
Experimental: tert-Butyl (6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)acetate 1 (10.00 g, 40.1 mmol) [2] was suspended in anhydrous pyridine (120 mL), heated to 80 ¡ãC for 30 min, then cooled to room temperature. 4-Methoxybenzoyl chloride (17.90 g, 100 mmol) was added in portions and the mixture was stirred for 18 h at room temperature, then evaporated in vacuo and the residue was coevaporated with toluene (3 x 50 mL). The residue was dissolved in dichloromethane (160 mL) and the solution was washed with 10% (w/v) citric acid (2 x 70 mL), dried (MgSO4) and evaporated in vacuo. The crude product was dissolved in dichloromethane (150 mL), trifluoroacetic acid (32 mL) was added, followed by water (1.6 mL) as a scavenger, and the mixture was stirred for 2 days at room temperature. The solution was evaporated in vacuo, coevaporated with toluene (2 x 50 mL), and acetonitrile (3 x 50 mL). The residue was thoroughly triturated with diethyl ether (5 x 50 mL), and filtered to give a white powder 2 (11.80 g, 90%), mp. 220 ¡ãC (darkens), 226 ¡ãC (decomp.) TLC: single spot. An analytically pure sample was obtained by recrystallisation from methanol (1500 mL of solvent was required for the above amount).
Mp. 231-236 ¡ãC. (lit. [3] 222-226 ¡ãC).
TLC: n-butanol-acetic acid-water: 4:1:1, Rf: 0.37.
1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 500 MHz, ppm, asterisks denote interchangeable assignments): 3.84 (s, 3H, OCH3), 5.12 (s, 2H, CH2), 7.07 (d, J=8.3 Hz, 2H, H-3', H-5'), 8.06 (d, J=8.3 Hz, 2H, H-2', H-6'), 8.45 (s, 1H, H-8*), 8.71 (s, 1H, H-2*).
13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 125 MHz, ppm, assignment based on decoupled and J-modulated spin echo experiments): 44.18 (CH2), 55.37 (OCH3), 113.59 (C-3', C-5'), 125.00 (C-5), 125.49 (C-1'), 130.44 (C-2', C-6'), 144.84 (C-8), 150.23 (C-4), 151.40 (C-2), 152.39 (C-6), 162.47, 165.00, 168.92 (2xCO, C-4').
ESI-MS (m/z): 328 ([M+H]+).
Anal. calcd. for C15H13N5O4 (327.295): C, 55.05; H, 4.00; N, 21.40; found: C, 55.23; H, 4.09; N, 21.31%.
References:
1. Z. Tim¨¢r, L. Kov¨¢cs, Gy. Kov¨¢cs, Z. Schm¨¦l, J. Chem.Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 2000, 19-26.
2. G. Ceulemans, A. van Aerschot, B. Wroblowski, J. Rozenski, C. Hendrix, P. Herdewijn, Chem. Eur. J., 1997, 1997-2000.
3. D.W. Will, D. Langner, J. Knolle, E. Uhlmann, Tetrahedron, 1995, 51, 12069-12082.
Sample availability: sample available from the authors.
© 2004 MDPI. All rights reserved.